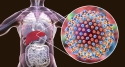
(RxWiki News) The link between viruses that cause hepatitis and the development of cancer is believed to be why several areas in Asia have higher rates of liver cancer. New research indicates that may not be the full story.
There are several factors in the research literature shown to increase liver cancer risk, mostly related to extremely heavy drinking, smoking, rare genetic conditions and viral infections that cause liver damage.
Researchers in Italy decided to study the link between hepatitis and liver cancer outside of Asia. After accounting for all other known factors that could influence the development of liver cancer, researchers concluded that family history alone was a significant risk.
"Ask your doctor about cancer screenings."
The research was summarized in a meta-analysis of nine different studies of case-control design, and four cohort studies for a total of 3,600 patients. Family history was found to increase odds of liver cancer by 2.5 times.
For people who tested positive for viral hepatitis as well as the family history, there was a 70-fold greater risk of developing cancer. Researchers felt it was important to verify the genetic relationship with liver cancer existed outside of Asian populations.
"There is a high incidence of liver cancer in southern Italy which is likely a result of a higher frequency of HCV in this area," stated Carlo La Vecchia, MD. "Our study investigated the relationship between family history and liver cancer in a Western population."
In conclusion, Dr. la Vecchia says,"Monitoring individuals with family history, particularly those with hepatitis markers, could help to identify HCC at an earlier stage, and hence potentially reduce mortality from HCC."
The study was published in the May edition of the journal Hepatology.
Financial conflict of interest was not disclosed to the public by the researchers.