A Guide to Childhood Vaccines
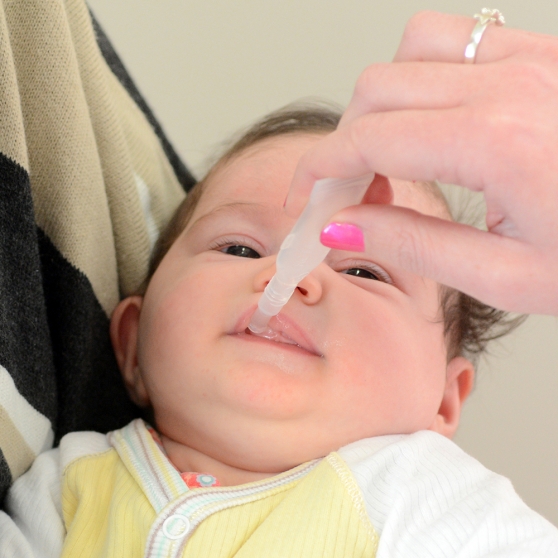
Rotavirus is a contagious virus that can cause inflammation of the stomach and intestines. Rotavirus is spread through a fecal-oral route. Symptoms include severe diarrhea, vomiting, fever and abdominal pain. According to the CDC, infants and young children are the group most likely to get rotavirus. The virus can cause severe dehydration and even death. There are two doses of the rotavirus vaccine given orally — the first when a child is 2 months old and the second at 4 months old.
Reviewed by:
Review Date:
July 23, 2015Citation:
Image courtesy of Seanlockephotography | Dreamstime.com Image courtesy of Designua | Dreamstime.com Image courtesy of Jarun011 | Dreamstime.com Image courtesy of Lucidwaters | Dreamstime.com Image courtesy of Alexskopje | Dreamstime.com Image courtesy of Attila Barabás | Dreamstime.com Image courtesy of Jean Paul Chassenet | Dreamstime.com Image courtesy of Sherry Young | Dreamstime.com Image courtesy of Rob3000 | Dreamstime.com Image courtesy of Designua | Dreamstime.com Image courtesy of Madhourse | Dreamstime.com CDC, "Chickenpox (Varicella): Vaccination" CDC, "Meningococcal Vaccine for Preteens and Teens" dailyRx News, "Back to School! Are You Ready?" dailyRx News, "Your Child's First 6 Months of Vaccines" dailyRx News, "Back-to-School Health" CDC, "HPV Vaccine - Questions & Answers" Medline Plus, "MMR Vaccine (Measles, Mumps, and Rubella)" Mayo Clinic, "Polio" Mayo Clinic, "Diphtheria" CDC, "Rotavirus: Vaccination" CDC, "Hepatitis A FAQs for the Public"
Last Updated:
July 23, 2015