Stroke Awareness
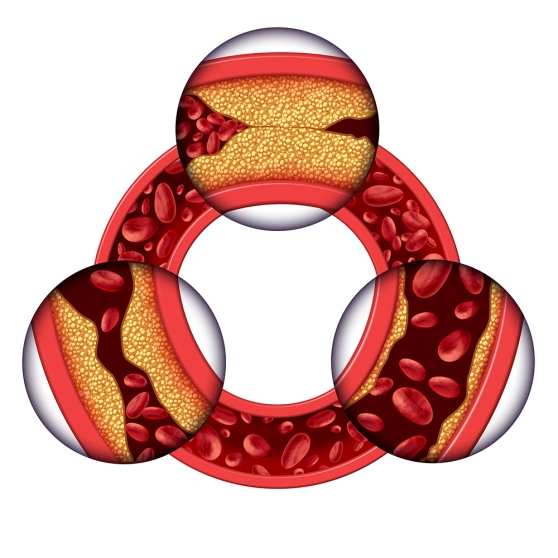
A stroke is commonly caused by a blocked artery (a blood vessel which carries blood from the heart) or the leak or burst of a blood vessel. Most strokes are classified as ischemic strokes. In an ischemic stroke, an artery to the brain becomes blocked or reduced. The cause of the blockage is usually a blood clot or plaque (a buildup in the walls of arteries). Strokes may also be classified as hemorrhagic strokes or transient ischemic attacks (TSA). In an ischemic stroke, a blood vessel in the brain ruptures or leaks. In a TSA, sometimes called a “mini-stroke,” symptoms of a stroke are present but these last less than five minutes and may not have longterm effects.
Reviewed by:
Review Date:
May 21, 2015Citation:
CDC, "Preventing Stroke: Healthy Living" Mayo Clinic, "Coping and support" American Stroke Association, "Stroke Treatments" National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, "How Is a Stroke Diagnosed?" Mayo Clinic, "Symptoms and causes" American Stroke Association, "About Stroke" American Stroke Association, "Spot A Stroke" Mayo Clinic, "Stroke Overview" Image courtesy of Skypixel | Dreamstime.com Image courtesy of Paulus Rusyanto | Dreamstime.com Image courtesy of Alila07 | Dreamstime.com Image courtesy of Paulus Rusyanto | Dreamstime.com Image courtesy of Skypixel | Dreamstime.com Image courtesy of Ikonoklastfotografie | Dreamstime.com Image courtesy of Timwege | Dreamstime.com Image courtesy of Andrew Bassett | Dreamstime.com Image courtesy of Ruslan Huzau | Dreamstime.com
Last Updated:
May 21, 2015